sequence of filter (kernel) applied to an image
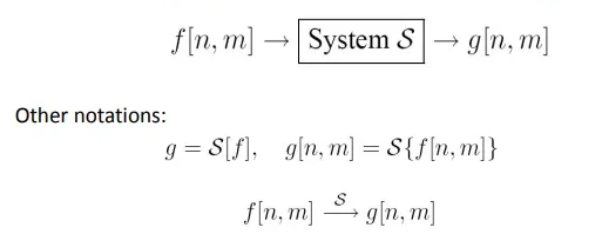
- unit that converts input
f[n,m]to outputg[n,m]- (n,m) - index into the function
- represents spatial position in the image
- (n,m) - index into the function
2D discrete system
- S is system operator, which maps inputs to outputs
Properties
- amplitude linearity
- superposition (linear combination) property
- *important - know how to prove if a system has this property
- other properties
- spatial properties
Key
A linear shift invariant (LSI) system is completely specified by its impulse response.
-
h can represent S
-
can make expression for g in terms of h
-
An image can be decomposed as a sum of impulses (sum of matrices for each pixel where all other pixels are 0)
-
SUM(pixel value * shifted impulse function)
- shift to get the delta 1 at the pixel
- the sum represents the input image
- this lets us use superposition (linear combination) property to see what the output g is
- decouples pixel value from the system by using impulse function
- to apply linear shift invariant (LSI) to an image = sum of element-wise multiplication of pixel value with system impulse response
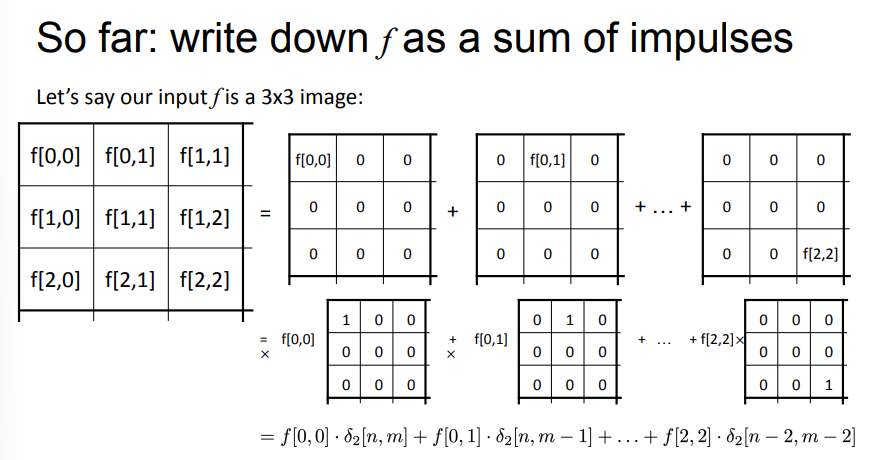
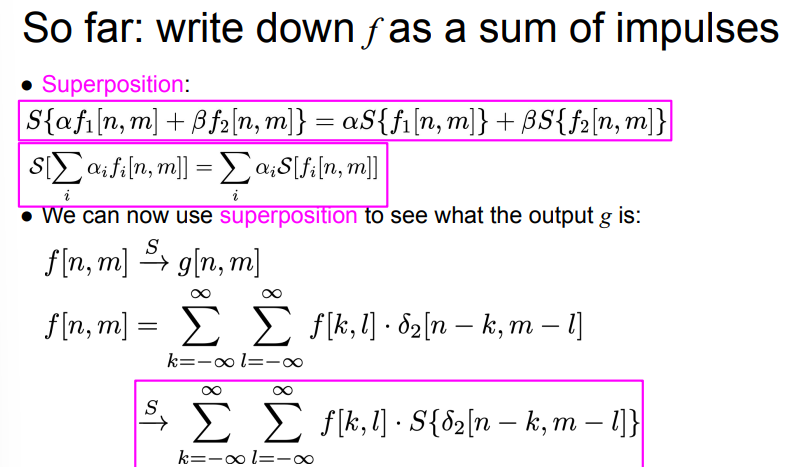
- to apply linear shift invariant (LSI) to an image = sum of element-wise multiplication of pixel value with system impulse response
- decouples pixel value from the system by using impulse function
Superposition means passing image to linear shift invariant (LSI) system = summing pixel.val * impulse response