- most widely used in CV for Edge Detection
- theoretical model: optimal when pixels have additive gaussian noise
- the first derivative of the gaussian DoG closely approximates the operator that optimizes the product of signal-to-noise ratio
- Suppress noise
- Filter with x,y derivative of the gaussian DoG
- Compute Gradient magnitude and direction
- Apply non-maximum suppression
- assures minimal response
- Reduce multi-pixel wide edges down to single pixel edge
- Use hysteresis thresholding and connectivity analysis for Edge Detection
result
-
connected edges, thin and non-redundant
-
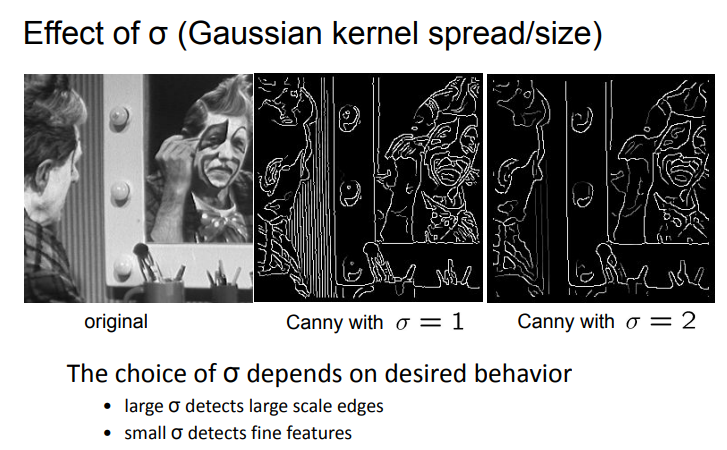
hyperparameter of gaussian filter (kernel) size